Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized how we interact with technology, offering a seamless connection between the physical and digital worlds. IoT devices, which form the backbone of this transformation, are increasingly ubiquitous, powering innovations across various sectors. This article delves into what IoT devices are, their components, functionalities, and the diverse applications that make them indispensable in modern life.

Understanding IoT Devices
Definition
An IoT device is any hardware that connects to the internet, either directly or indirectly, and collects, sends, or receives data. These devices range from simple sensors that monitor environmental conditions to complex systems like smart home appliances and industrial machines.
Some have different processors like arm and amd, or just generic processors. The idea is to be connected to the cloud and possibly have a web interface as backend in the cloud from where you can interact and control it.
Components of IoT Devices
- Sensors/Actuators: Sensors collect data from the environment, such as temperature, humidity, motion, light, and other physical parameters. Actuators perform actions based on the data received, such as turning on a light or adjusting a thermostat.
- Connectivity: IoT devices require a means to transmit data to and from other devices or centralized systems. Common connectivity options include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, and cellular networks.
- Data Processing: Some IoT devices have built-in processors that perform data analysis and processing locally. Others send data to centralized cloud services for processing.
- User Interface: This can be a physical display on the device, a mobile app, or a web interface, allowing users to interact with the device, monitor data, and control operations.
- Power Supply: IoT devices can be battery-operated, use solar power, or be plugged into an electrical outlet, depending on their intended use and energy requirements.
How IoT Devices Work
IoT devices operate through a series of steps involving data collection, transmission, processing, and action. Here’s a typical workflow:
- Data Collection: Sensors gather data from their surroundings.
- Data Transmission: Collected data is sent to a gateway or directly to the cloud via the internet.
- Data Processing: Data is processed locally on the device, at the gateway, or in the cloud to extract meaningful information.
- Action: Based on the processed data, an action is taken either automatically by the device or manually by the user through an interface.
Applications of IoT Devices
IoT devices are used across numerous fields, significantly enhancing efficiency, convenience, and connectivity. Below are some key sectors where IoT devices are making a substantial impact.
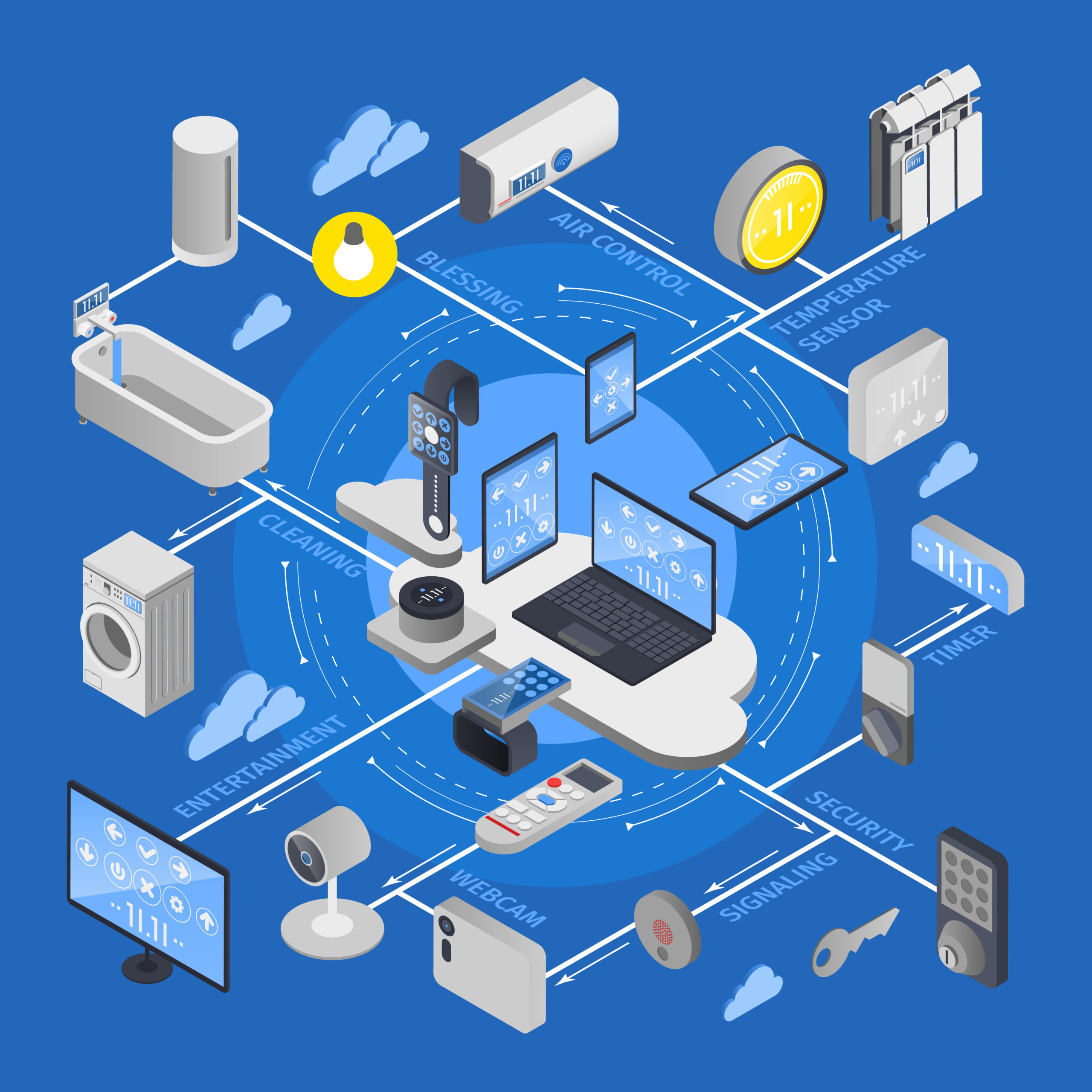
Smart Homes
IoT devices are transforming homes into smart homes, where various appliances and systems can be controlled remotely. Common smart home devices include:
- Smart Thermostats: Adjust heating and cooling based on user preferences and occupancy patterns.
- Smart Lighting: Automate lighting schedules and intensity based on time of day or presence detection.
- Smart Security Systems: Include cameras, doorbells, and locks that provide real-time surveillance and remote access.
- Smart Appliances: Such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens that can be controlled via smartphone apps.
Healthcare
In healthcare, IoT devices are improving patient care, streamlining operations, and enhancing medical research. Examples include:
- Wearable Devices: Track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, providing real-time health monitoring.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Devices that allow healthcare providers to monitor patients’ conditions remotely, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
- Smart Medical Equipment: Includes connected inhalers, insulin pumps, and other devices that provide timely medication and alerts.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) focuses on using IoT devices to improve manufacturing and industrial processes. Key applications include:
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors monitor machinery for signs of wear and tear, predicting failures before they occur, thereby reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Asset Tracking: IoT devices track the location and status of assets in real-time, improving inventory management and logistics.
- Environmental Monitoring: Sensors monitor conditions such as temperature, humidity, and air quality in industrial environments to ensure compliance and safety.
Agriculture
IoT devices in agriculture, or smart farming, enhance productivity and resource management. Applications include:
- Precision Farming: Sensors and drones collect data on soil conditions, weather, and crop health, enabling precise application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Livestock Monitoring: Wearable devices track the health and activity of livestock, providing insights into their well-being and productivity.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Automated systems that adjust water usage based on soil moisture levels and weather forecasts.
Transportation
In the transportation sector, IoT devices are improving safety, efficiency, and user experience. Examples include:
- Connected Vehicles: Cars equipped with sensors and internet connectivity that provide real-time traffic updates, navigation, and diagnostics.
- Fleet Management: IoT devices track the location, speed, and maintenance needs of commercial vehicle fleets, optimizing routes and reducing operational costs.
- Smart Infrastructure: Traffic lights, parking meters, and toll booths equipped with IoT technology to manage traffic flow and enhance urban mobility.
Benefits of IoT Devices
The proliferation of IoT devices brings numerous benefits across different sectors:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation and real-time data processing streamline operations, reducing manual intervention and errors.
- Cost Savings: Predictive maintenance and optimized resource usage lower operational costs.
- Improved Decision-Making: Access to real-time data enables informed decisions, improving outcomes in various applications.
- Increased Convenience: Remote monitoring and control of devices enhance user convenience and flexibility.
- Better Health and Safety: IoT devices contribute to improved health monitoring and safety measures, particularly in healthcare and industrial environments.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, IoT devices also present several challenges:
- Security: The vast number of connected devices increases the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. Ensuring robust security measures is paramount.
- Privacy: IoT devices often collect sensitive data, raising concerns about user privacy and data protection.
- Interoperability: With various manufacturers and standards, ensuring that different IoT devices work seamlessly together can be challenging.
- Scalability: As the number of IoT devices grows, managing and scaling the infrastructure to support them becomes increasingly complex.
- Power Consumption: Many IoT devices rely on batteries, requiring efficient power management to ensure long-term operation.
Future of IoT Devices
The future of IoT is bright, with continued advancements expected to drive further innovation and integration across sectors. Some key trends include:
- 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G networks will enhance connectivity, enabling faster data transmission and more reliable connections for IoT devices.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to where it is generated (on the edge) will reduce latency and bandwidth usage, making IoT applications more efficient.
- AI and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning with IoT devices will enable more intelligent and autonomous systems, capable of learning and adapting over time.
- Blockchain: Using blockchain technology can enhance security and transparency in IoT systems, providing secure data transactions and storage.
- Sustainability: IoT devices will play a crucial role in promoting sustainability by optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and supporting renewable energy initiatives.
Conclusion
IoT devices are transforming the way we live and work, offering unprecedented connectivity and automation. From smart homes and healthcare to industrial processes and agriculture, the applications of IoT are vast and varied. While challenges such as security, privacy, and interoperability remain, the ongoing advancements in technology promise to address these issues, paving the way for a more connected and efficient future. As IoT continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly unlock new possibilities and reshape the landscape of modern technology.


Leave a Reply